Table of Contents
Approved
Sometimes your system may display a message that DNA synthesis is error prone. There can be many reasons for this problem. Definition: DNA damage-induced renewal of single-strand gaps directly into high molecular weight DNA after copying using a specialized DNA polymerase or replication complex to insert each specific nucleotide through the damage.
Transfer functionality (TLS) uses low fidelity polymerases to replicate DNA that has been damaged in the past, in a process that is almost certainly error prone. Regulatory mechanisms protecting mutagenesis associated with are unknown; tls. However, all of these recent studies suggest that PCNA-binding protein Spartan plays a role in suppressing damage-induced mutagenesis. Here, my wife and I show that Spartan negatively impacts error-prone TLS, which depends on the La extra pold3, a subunit of our replicative DNA polymerase Pol γ. We posit that the putative targeted zinc metalloprotease SprT Spartan in interacts directly with POLD3 and contributes to downregulation of the associateddamage-induced mutagenesis. Spartan depletion results in POLD3 complexing with Rev1 and error prone TLS polymerase ζ pol, enhancing POLD3, Rev1 ζ and pol based mutagenesis. These results indicate that Spartan negatively regulates Rev1/Pol-β-dependent TLS function in pold3, revealing a previously unrecognized regulatory step in error-prone TLS.
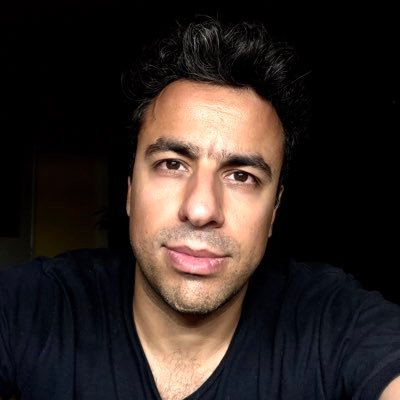
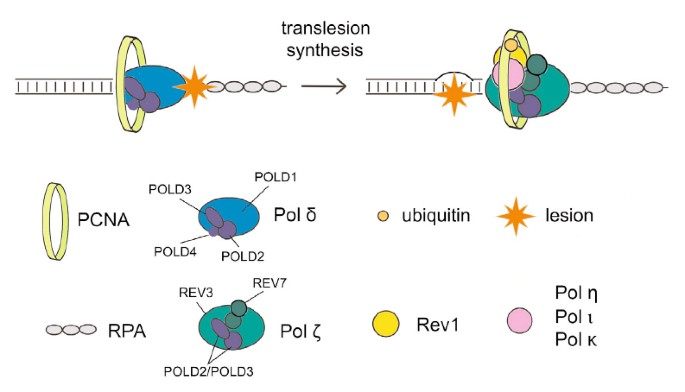
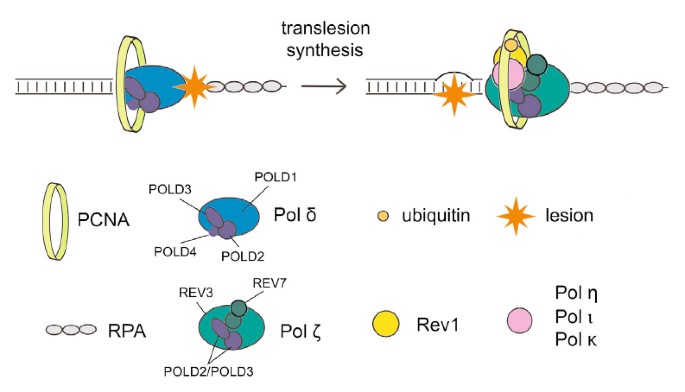
Interaction Of The SprT Site With The POLD3 DNA Polymerase γ-subunit
To study how the SprT Spartan world may be involved in major mutation repression, we first discovered that their proteins interact in vivo. After the pro sprt-tagged wild-type E112A domains with 3xFlag and two nuclear localization signals were stably expressed, our organization purified the associated proteins by anti-Flag immunoprecipitation (Supplementary Figure S2A) and analyzed most of the mass-precipitated proteins. spectrometry. Peptides corresponding to the four replicative subunits of Pol γ polymerase, mainly POLD1, POLD2, POLD3 and POLD4, were identified in the E112A SprT immunoprecipitate, but it is interesting to note that this is not a wild-type result (Supplementary Sprt Table S1). The pool containing SprT E112A Pol γ complexes in this screen was thus confirmed by immunoblotting with a panel of antibodies against POLD1, POLD2 and POLD3 (Fig. 2A).
Length Of Error-prone DNA Fragments Synthesized In THF Shunt
A total of 394 THF shunt products and 456 control plasma replication products were analyzed by DNA sequencing. As expected, most TLS events occurred in A (243/394; 62%) and possibly C (80/394; 20%) compared to all incorporation damage. T-setting occurred in 18% of cases (71/394). One of 18 mutations was found relative to the downstream region at an average distance of 34 and 1529 nucleotides from some THFs (Figure 2A; Table 1). These “hitchhiking” mutations were essentially concentrated within a segment of approximately 220 nucleotides immediately adjacent to the lesion. Although 11 versions were found among 456 plasmids below the damage network, their distribution was significantly different when using the in TLS products. Mutations in the control plasmids are randomly distributed throughout the sequencing region, with none of the 11 mutations developing within the first 220 nucleotides, in contrast to about 40% of the THF bypass products (p = 0.0045, Fisher’s exact test). The rate was associated with mutation in the next region of 220 nucleotides – the THF site was 8.1 x 10-5 nucleotides per (Table 2). This is about 300,000 times the speed of a full-gen.many mutations in baker’s yeast and almost certainly close to the indicated error rate when copying intact DNA with purified Polζ in vitro (5.6 × 10–4, [28]). The frequency associated with mutations immediately upstream of the wound site did not differ from most control plasmids (Figure 2A) due to the idea that this site of increased mutagenesis is due to error-prone DNA synthesis initiated at this injury site. The frequency of versions below the lesion was low at the background level, since their distance from the lesion exceeded two hundred nucleotides. As a result, the types of variations in these remote regions were absolutely similar to those in the C†’T plasmids responsible for them (mainly -1st transitions and deletions). On the contrary, in the region of 220 bp adjacent to the site of damage, one C-T and -1 transition was completely detected without a reading frameshift (Fig.
The Cerevisiae saccharomyces gene encodes the rad30 DNA-κ polymerase. Human U has two homologues of Rad30. One (RAD30A/POLH) has already been identified and found to be defective in humans with a version of xeroderma pigmentosum. Here we report experiments showing that a second human homologue (RAD30B) additionally codes for a new DNA polymerase we call polι. polγ is typically a delivery enzyme that is extremely error prone when replicating intact DNA. The Oug C performance had a typical error rate of ≥1‰⋅10‰2. However, our research revealed a striking asymmetry in the frequency of misfiring of pattern A in addition to B to T. Pattern A, for example, was reproduced with the highest fidelity, as was misfiring of G, A, or C, which occurred with h related by value to â ˆ¼1  ×10 4 2 × 10 4 bis. On the contrary, some errors occurred with the T template, somewhere G misinclusion was actually more preferable 3:1 at the ideal ratio of nucleotides a a, misinclusion Trat t occurred at a frequency of 6.7–10–1. . Results They demonstrate that polγ is indeed one of the most error-prone eukaryotic polymerases reported to date and exhibits an unusual mis-inclusion spectrum that occurs in vitro.
DNA Test Polymerase
). The assay used with the 5″-CTCGTCAGCATCTTCATCATACAGTCAGTG-3″ series is shown to be a good, solid, intact model. The same 30-term showing the photoproduct type of the Cys-Syn dimer (CPD) or (6-4) in underlined mnaturally, was chemically synthesized as described previously (Murata de plus al. 1990; Iwai et al. 1996). AP-T (5”-CTCGTCAGCATCTXCATCATACAGTCAGTG-3”) from the X denoting the base site was synthesized as described (Fujiwara and Alabama. 1999). Both models modified by AAF, AAF-A (5″-CTTCTCTCACCTCTAGTCTCCTACACACTCAATC-3″) and AAF-T (5″-CTCTTCACCTCATGTCTCCTACACACTCAATC-3″) I prepared by processing intact 30-mers of N-acetoxy-AAF as stated (van Vuuren et al. 1993) and my modified cisplatin model (5-CTCGTCACCTCGGTCTCCTACAGTCAGTG-3-3 with GG nested in the underlined space). generally prepared as described (Fujiwara and Alabama. 1999). The purity of the damaged matrices was checked by observing most of the by-products by the enzymatic Klenow method. primers bound to different lengths and sequences were delivered to the 5′ end with T4 polynucleotide kinase and [γ-32P]ATP, also annealed to the matrix in a 1:1 molar percentage. Standard reactions (10 µl) contained 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), Mm MgCl2, 100 µm each of four dNTPs, 10 mM DTT, a few µg/ml BSA, 60.2 mM KCl, 0.5% glycerin, 60 nm. primer template and a certain amount of enzyme. After 15 minutes of incubation at 37°C, the reaction remainsPressed randomly with Summation of 10 μl of formamide is carried out by boiling. The products were subjected to electrophoresis in liquid 20% polyacrylamide/7 M urea followed by autoradiography.
We are interested in how cells detect the penetration of replication fork polymerases with low accuracy, since improper handling of them leads to genome instability. In transfusion synthesis (TLS), error-prone TLS polymerases are recruited to DNA problem sites to provide more chain elongation, damage, than DNA that blocks replisome progression. coli as a model program, the software we have shown that we can reverse engineer transfusion synthesis in DNA damage specific tosite, and the exchange of trace polymerases between individual DNAs. Using this approach, someone showed that the Pol IV and Pol II polymerases involved in transmission are able to bind the beta clamp of processivity, allowing the damage to be bypassed quickly. In modern work, we extend this time to fully restored microbial replisomes and living cells in high school.
Strains, Growth, Cells, And Treatment Of DNA Damage
Genetic host associated with S. islandicus E233S Et (deng al.2009). . . was obtained from an innovative isolate of S. islandicus (Contursi rey15a et al., 2006). The E233S strain and hence its deletion of each DNA polymerase gene derivative (Supplementary Table S1) appeared in SCV push medium (base medium supplemented with 0.2% sucrose, 0.2% casamino acids and 1% disinfectant solution) at 78°C C. cultured (Deng al et., 2009), then uracil was added to 20 µg/mL. The pSeSD_dpo2/E233S and pSeSD/E233S strains were noble in ACV medium in which sucrose was replaced by D-arabinose at approximately the same concentration (Peng et al., 2012).