Table of Contents
Last week, some readers reported that they learned how to enable APIP in Windows 7.
Approved
Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) is a feature of Windows-based operating systems (included with Windows 98, ME, 2000, and XP) that allows a computer to automatically use an IP address for itself, in most cases not a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server (DHCP) is available to perform this normal function.
More Information
A Windows computer configured to use DHCP can assign itself a full Web Protocol (IP) address when a DHCP server is often unavailable. It’s mocan happen, for example, on a network without a DHCP server, or when the DHCP server is temporarily unavailable for service.
This article describes the easiest way to use Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) auto-addressing without always having a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server on the network. The system versions listed in the “Applies to” section of this article will receive a feature called Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA). With this feature, an awesome Windows computer can assign itself an IP (Internet Protocol) address in case a DHCP server is not available or will not be present on the network. This feature makes it easy to set up and maintain a small local area network (LAN) using TCP/IP.
How It Works
Similar In addition to Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003 allows you to configure a new alternate IP configuration for a DHCP-enabled computer that cannot communicate with a DHCP server. If your good Windows Server 2003 computer can’t get or renew a DHCP contract, it will configure itself with an incredible Class B network IP address of 169.254.0.0. This can be used to provide temporary (albeit limited) mapping access when your DHCP server is unavailable, or to provide a principles-based access solution for a small workspace with limited connectivity needs where a DHCP forum may not be available.
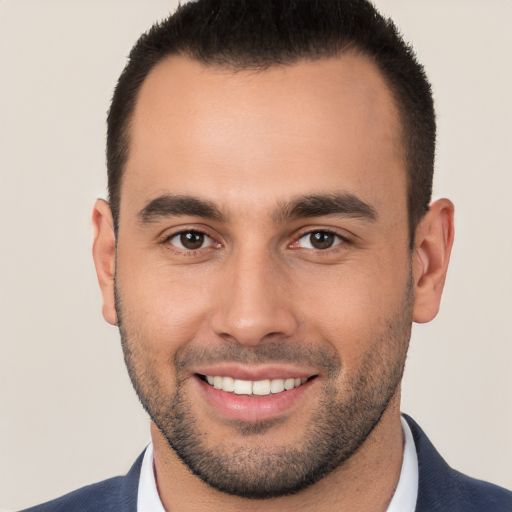
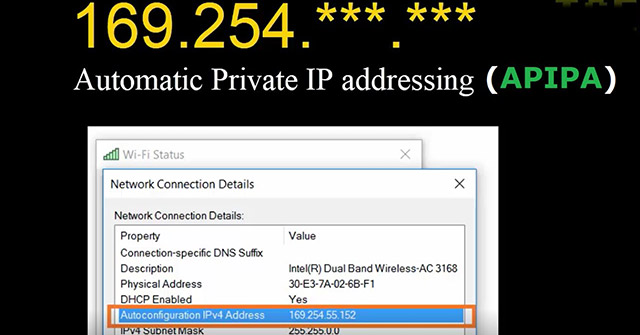
When a Windows computer cannot obtain a valid IP address from a DHCP server, the operating system automatically assigns it an automatically generated Windows private IP address called APIPA. This automatic private IP address is close to the range 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254. In short, we can say that almost all IP addresses, unlike (169.254.X.X), are APIPA, and this shows that not all of your computers are connected to many networks. Since APIPA (169.254.X.X) is a brand new private IP address, your computer will probably not interact with other specific computers connected to the network (connected to your own DHCP server). If you want your own computer to communicate with othersservers on the network, you must change the IP address to 169.254.X.X, fixing our own problems that prevent your computer from getting a valid IP address as a DHCP server. This guide explains the main causes of APIPA and how to resolve them.
How APIPA Works
Networks configured for complex addressing rely on a DHCP host to manage the local IP addresses offered by the pool. When a Windows client device tries to join a local computer network, it contacts a DHCP server to claim ownership of its IP address.If the DHCP server stops working or a network error interferes with someone’s request, this process can easily fail.
Which IP Address Corresponds To The APIPA Address Range?
169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.IP 254.The apipa address range is definitely 169.254. 0.1 to help you 169.254. 255 254. When an APIPA IP address is definitely discovered for a remote Desktop Central computer, Desktop Central agents detect that that particular server page is hard to reach.