Table of Contents
Sometimes your system may display the error “You may see Software Raid 5 on Windows Server 2003”. There are several reasons that can cause this problem.
Approved
g.RAID 5 is a legacy system of independent disk configurations that uses disk striping with parity. Since data and parity are distributed evenly across all hard drives, a single hard drive is not a bottleneck. Striping also allows users to recover numbers in the event of a CD or DVD failure.
g.
There Here are some of these options for setting up your RAID environment. You can use software RAID or hardware RAID. Software RAID should be cheaper because you don’t have to buy anything else, so it only works at certain times and the performance is not very good. You cannot simply switch from one RAID type to another. If you want to change, you need to do the following:
The key to testing is to determine which RAID solution is best for a good reliable environment. This section discusses the differences between hardware and software RAID, and when it is best to use a particular RAID over another.
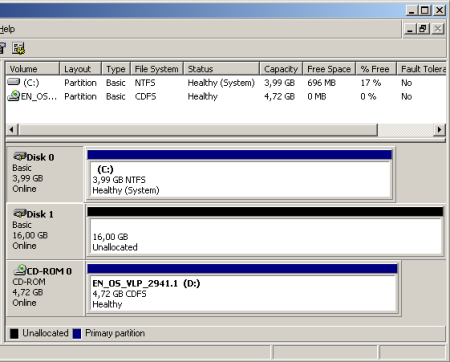
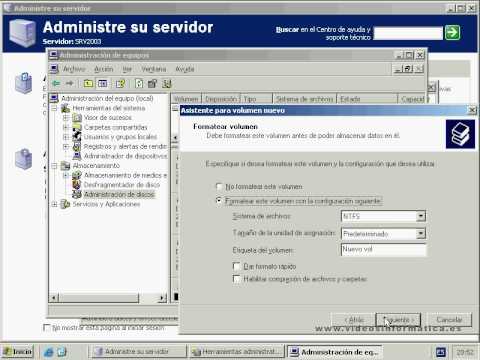
Windows 2003 Server RAID Information
RAID of your five works with a variety of file systems including FAT, FAT32, and NTFS. In principle, almost all arrays are widely used in a commercial environment, but if you are an active userIf you are interested in protecting data and improving system performance, you can create a RAID Five in Windows 10.
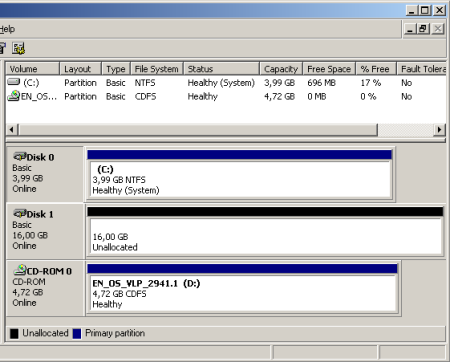
Computer RAID in Windows 2003 is software RAID. In software RAID, all physical hard drives are usually presented to the operating system, even if they exist, and the operating process is managing them as RAID. The advantage is that software RAID is integratedinto the operating function. The downside is that the operating system fully supports RAID volume. In addition, there are limitations and software RAID that does not apply to hardware RAID. With software RAID, you won’t have many RAID options available. Windows Server 2003 only supports three RAID capacities: RAID 0, RAID One, RAID, and 5. We’ll cover both in more detail in the new sections.
A hard drive with a RAID level of 0 is striped. A RAID 0 volume in Windows Server 2003 is called a specific aggregate volume. This version of RAID does not provide fault tolerance. It is sometimes said that RAID 0 is really “AID” when it comes to wanting “RAID” because it does not provide data redundancy. As I said, it provides the best performance out of all RAID levels, and that is definitely its goal. Level 0 can be implemented both in software and as a hardware solution and is supported by all controllers.
Because the operating system must be loaded before initializing and allowing access to the striped area, the layer 0 bay cannot be used for loading or wall surfaces of the system. RAID 0 should be created when you are trying to get the best performance out of your disks. Level 0 is best for when computer files are not business critical or are continuously backed up on a regular basis. This is useful for streaming audio / video, games and additional applications where needed. RAID level 0 Windows Server 2003 works with two or more hard drives, up to a maximum of 36 hard drives.
RAID Level 1
raid 1 uses file mirroring. A RAID Level 1 depth in Windows Server 2003 is often referred to as a mirrored volume and consists of a pair of identical hard drives. An exact copy of the data is written to be written to the hard disk in one go. This version of RAID provides fault tolerance and is the only software RAID level in Windows Server 2003 that can be used for boot and application partitions. Level 1 is the fastest RAID implementation that can be implemented as a software or hardware RAID solution for PC.
RAID 1 should be used a little more often if you need fault tolerance for athletic shoes and / or system partitions, or if you need fault tolerance and two hard drives. Level 1 is the most expensive form of RAID in Windows Server 2004 because only 50 percent of the space that needs to be automatically obtained is used for data.
RAID Level 5
RAID level 5 uses hard disk striping with parity. The RAID level of a Windows 5 volume in Server 2003 can be referred to as a RAID 5 volume. Since a RAID-5 volume is striped with the hard drive, it is not used for the bootable system partition because the operating method must first be loaded into in order to initialize the volume and make it available. Parity information is spread across multiple disks, and because of a given block of data, parity is usually always on the other disk using disks that hold the material itself if only one CD in the array fails.
RAID-5 volumes must also contain at least three hard drives for up to 37 hard drives. Are you upYou should use a RAID 5 level because you want the fault tolerance with the best performance and disk utilization that a RAID 1 level can provide. One of the most popular RAID implementations is a pair of RAID. However, the Five Tips RAID software is significantly slower than its hardware counterpart due to the overhead associated with computing the parity information. This is better for read-intensive applications than for write-intensive applications.
Hardware RAID
As the name suggests, hardware RAID uses convenient hardware to create RAID arrays. A RAID controller will be added to your current server. The controller takes over the management of the RAID and databases. This improves performance by eliminating this additional load on the operating system. It also removes many of the disadvantages associated with software RAID.
Since a RAID controller represents RAID to most operating systems as a hard drive, someone might be using RAID 0 volumes and therefore RAID 5 for sneakers and system racks Lovers. Hardware RAID gives you many other RAID settings to choose from, including the following:
• RAID 2 splits data at a bit level and splits it into two types of hard drives: Extra hard drives with data Redundant hard drives where redundant parts are calculated using Hamming codes (Error Correction Code or ECC design). Not often used due to cost and complexity. Requires a dedicated RAID controller card.
– RAID 3 data is partitioned at the byte level and spread across multiple hard drives, with one personal hard drive serving as a dedicated hard drive with parity. Requires a RAID controller; Excellent material for handling very large files.
– RAID 4: Data is stripped across multiple disks in blocks (instead of bits or possibly bytes) and uses the same dedicated disk. Requires a hardware RAID controller; used. for the same applications in RAID 3 and 5.RAID
• Six to eight stripes of data across multiple hard drives in blocks such as RAID 4 and 7, but one is created for each stripe New repeating sets. RAID is more fault tolerant than RAID 5 because the program can recover data if the other two hard drives in the array fail and write performance is not as good. Requires a hardware-dependent controller; used for critical data requiring increased fault tolerance.
Approved
The ASR Pro repair tool is the solution for a Windows PC that's running slowly, has registry issues, or is infected with malware. This powerful and easy-to-use tool can quickly diagnose and fix your PC, increasing performance, optimizing memory, and improving security in the process. Don't suffer from a sluggish computer any longer - try ASR Pro today!

• RAID 7 Implementing a computer-owned RAID set by Storage Corporation. Uses a tiered cache and a special template for array management. Unbelievable specialized equipment required; offers very impressive performance.
• Nested raid level tables that use a combination of individual heights. For example, use RAID levels 0 + 1 as well as 1 + 0 (also called 01 10) and / or “mirrored stripes” or “striped mirrors”. Level 0 + 1 creates a set of red stripes and then creates a separate stripe, so you have 3 sets of identical stripes. Level 1 + 0 whip data on mirror sets. This allows you to take advantage of the performance benefits associated with level 0, as well asNot with a Level 1 responsibility tolerance. Other RAID storage levels include 5 + 3 (also 53), 3 + 0 (30e). ), 0 + 5 (05), 5 + 0 (50), (15) 1 + 5 and 5 + 1 (51).
The only major drawback to hardware RAID is its cost. Server-grade RAID consoles typically cost up to $ 750. This can add up quickly if you now have a large number of servers.
Best Practices For RAID
Once the question of RAID volume usage is answered, the public must determine which solution best suits your needs. Will it be a general purpose bus RAID or software RAID? Hard drive striping or hard drive mirroring? How should your family put him there? are that there are no hard and fast rules, only recommendations. Here are some general guidelines to keep in mind when configuring RAID volumes:
• Always use hardware RAID as it provides good performance.
• Try to use identical hardware components for all of your servers. This makes disaster recovery easier.
• Always keep on hand speciale hard drives. If you lose any of this (on most RAID levels), someone will be out of range for acceptable performance levels. You should be able to remove and repair faulty hardware as quickly as possible. … (This also applies to software RAID.)
– Always back up your data before to update the firmware in the controller raid.
– Use RAID-5 for hard drives with large databases (such as Exchange and SQL servers).
• Use aggregated volumes on the hard drives of the database servers that contain transaction logs (for demonstration, Exchange and Server) sql.
• Use striped volumes for hard drives that are used to buffer the printer.
Test Day Tip
Whenever Microsoft refers to RAID in its research, always assume it is software RAID, unless specifically referred to as hardware RAID.
The software to fix your PC is just a click away - download it now.
Open Settings in Windows 10.Click System.Click Storage.In the “Advanced Storage Options” section, select the “Disk Spaces Management” option.Click on the answer. Create a new pool and new space.Select disks (at least three) to create the storage pool.
Microsoft is ending support for the main operating system Windows Server 2003 on J. [1] After this date, this product will no longer be available: Security glitches that help protect PCs from toxic viruses, spyware, and other malicious packages.