Table of Contents
Here are some easy ways that can help you fix a kernel mode user mode problem.
Approved
g.A process runs in operator mode and kernel mode during its life cycle. User mode is the normal mode in which these processes have limited access. While kernel mode is undoubtedly the preferred environment, where a process has unrestricted access to system resources like hardware, hard drive, etc.
g.
Approved
The ASR Pro repair tool is the solution for a Windows PC that's running slowly, has registry issues, or is infected with malware. This powerful and easy-to-use tool can quickly diagnose and fix your PC, increasing performance, optimizing memory, and improving security in the process. Don't suffer from a sluggish computer any longer - try ASR Pro today!

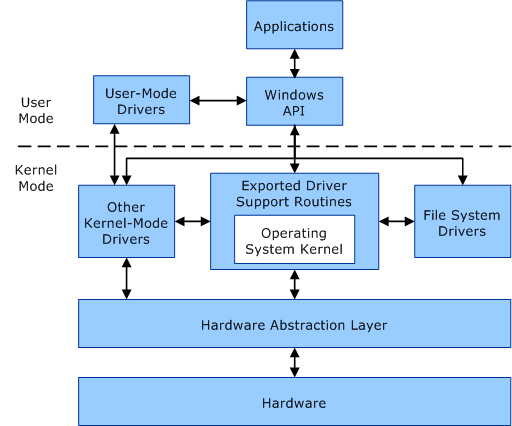
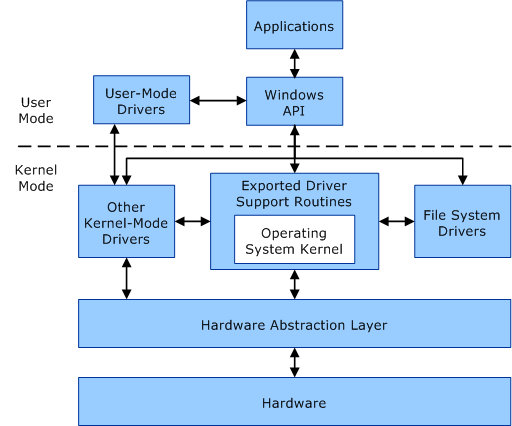
The processor in a Windows mainframe has two paired modes: user mode and kernel mode.
The product switches between the two modes depending on the rule executed by the processor. Applications are used in user mode, and the kernel of an operating system component runs in kernel mode. Although many drivers run the kernel in user mode, some drivers can be processed in user mode.
Custom Mode
When you run an application in user mode, Windows creates a dedicated application to handle the application. The plan provides the application with a public address in virtual space and an exclusive descriptor table. Since the app’s confidential address space is private, it is the only app that cannot modify your data in another app. Each application is launched remotely and in the event of an application crash, the crash is limited to which application. The crash usually does not affect the operation of other applications and the system.
Apart from customization, virtual address space outside of the application’s user mode is limited. A PC in user mode cannot access the addresses reserved for the operating system. Limiting the email address space for user-mode use prevents an application from modifying and potentially corrupting critical process data.
Kernel Mode
All code executed in The kernel uses a single virtual memory address. This means that any type of kernel-mode driver is not isolated from other types of drivers and from the operating system itself. If a kernel-mode driver inadvertently sends articles to the wrong virtual address, information and facts belonging to one operating group or another driver can be compromised. When a kernel-mode driver fails, all of our system operations fail.
Most production systems have a method showing CPU usage. Windows, this method is Task Manager.
CPU utilization is mainly represented by a simple percentage of CPU time spent in non-idle activities. But this is a little oversimplified. In every modern system, the processor actually has to pay for time in two very different modes:
- Kernel mode
In kernel mode, the running promo code has full and unlimited access to the base material. He can provide any link to instruction CN and almost any memory address. Kernel mode is mostly reserved at the lowest level and is most dependent on the functions of the operating system. Kernel mode crashes are catastrophic; he or she will shut down the entire computer.
- Custom mode
In user mode, the execution code does not have the ability to directly access reference hardware or PC memory. User-mode code must be delegated by the system using an API to access hardware or memory. With the protection provided by this type of isolation, user mode failures can always be corrected. Most of the code that runs on any computer is executed in PC operator mode.
It is possible to enable the display of the kernel time in the task manager, as in the screenshot above. The green line is the total processor time; red definitely indicates core time. The gap between two users is time.
These two modes are, of course, just designations; They are applied by the CPU hardware. When the builder of theUser mode tries to do something outside of its jurisdiction — for example, speak, access a privileged CPU instruction, or otherwise alter memory that it does not have access to — a fixable omission occurs. Instead of crashing your entire system, only a specific implementation crashes. This is a precious user mode.
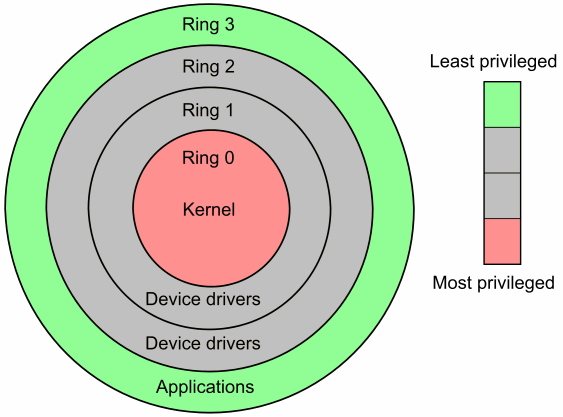
In fact, the x86-CPU offers hardware with four rings of protection: 0, 1, 2, and 3. Usually only rings (core) 0 and 3 (custom) are used.
Now, if we’re just using two electrical and artistic ribbons, it’s a little tricky to figure out where the device drivers should go – the code that usually allows us to use our video cards, keyboards, mice, printers, and so on, etc., etc. E. Do these drivers run in kernel mode for maximum performance or, if that fails, in user mode for maximum stability? On Windows, the answer is at least the one by which it is determined. Device drivers can run in a custom kernel or mode. At the same timeIn some cases, most drivers must bypass the user-side barrier, with the exception of video card drivers, which require kernel-mode performance. But that, too, has always changed; In Windows Vista, graphics drivers are divided into “Users” and “Partitions” kernels. Perhaps this is why complaining players play Vista about 10% slower.
The line between these regimes is still absurdly blurred. What code should I run in user mode? What code should I run in kernel mode? Or maybe we are unlikely to redefine land as a zone – the rise of virtualization has led to the creation of a new ring that follows everyone else, ring -1, which we know today as x86 device virtualization.
User Mode is certainly in the public domain of the Internet, but you have to pay for it. The transition between user mode and therefore kernel mode is expensive. Very expensive. This is why, for example, software that handles exceptions is slow. Exceptions are related to transitions from the modeto the core. Of course, we have so much power now that we rarely have to worry about the strength of the adjustment, but if you end up wanting strength, you will certainly start worrying about those things.
Probably the most public example of a custom line or core redesign is in web servers. Microsoft IIS 6 ported much of its core functionality into a kernel routine, especially after the desired open source web server used kernel mode to showcase a major industry win. It was kind of a war, completely unfounded if you ask me, since all core optimizations (in both camps) are ideally applicable to static HTML content. But this is the path of just wars, milestones or other attractions.
The strict separation of processor code between user mode and kernel mode is completely transparent to most of us, but most likely it will literally be the difference between a computer that constantly crashes and a computer that crashes catastrophically. It’s just for us, the authors of the code with increased emergencyost, I like to “progress”. On behalf of many programmers around the world, I would like to testify about the user gratitude mode. You are burning!
The software to fix your PC is just a click away - download it now.
In kernel mode, the executable code has full and unrestricted access to the underlying hardware type. It can execute almost any CPU instruction and reference any RAM address. Kernel mode is usually suggested for the lowest-level and most reliable operating system in the operating system.
The only way for the user room in your home application to explicitly initiate a switch to kernel mode during normal operation is to tell the system to use open, read, write for help. A software interrupt / exception (SWI) is thrown whenever a user application calls some of these system call APIs with appropriate restrictions.