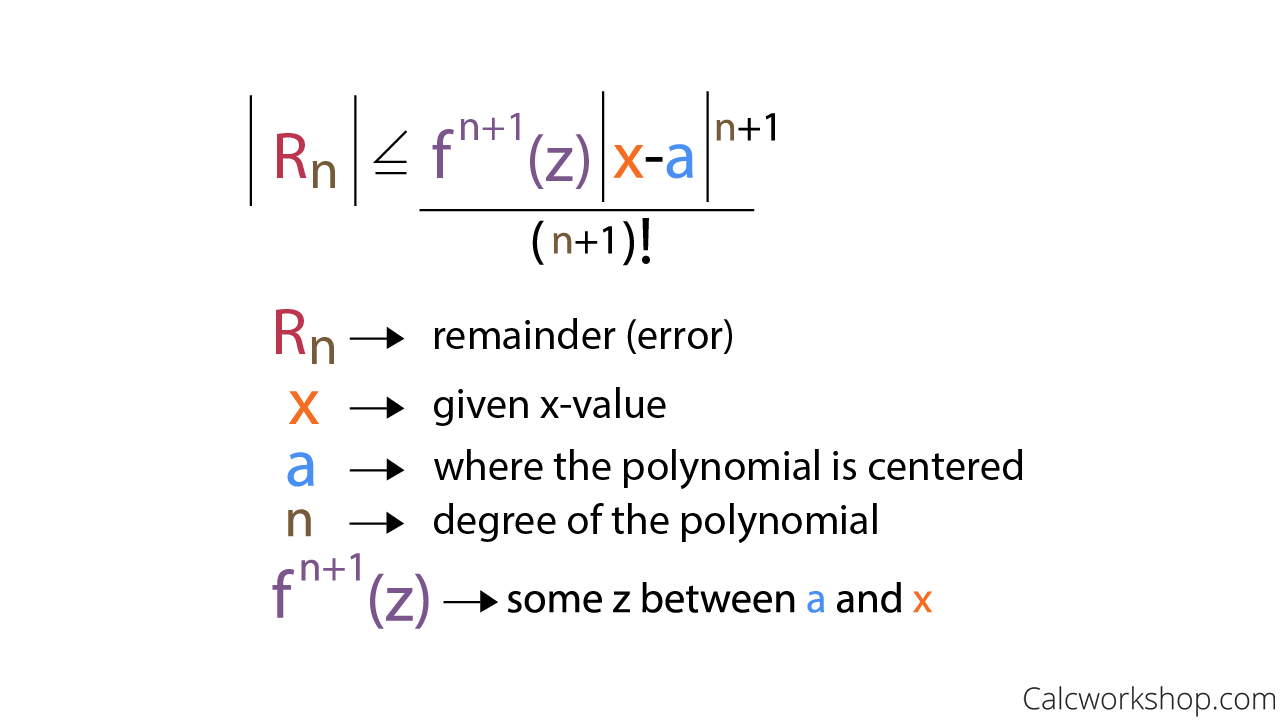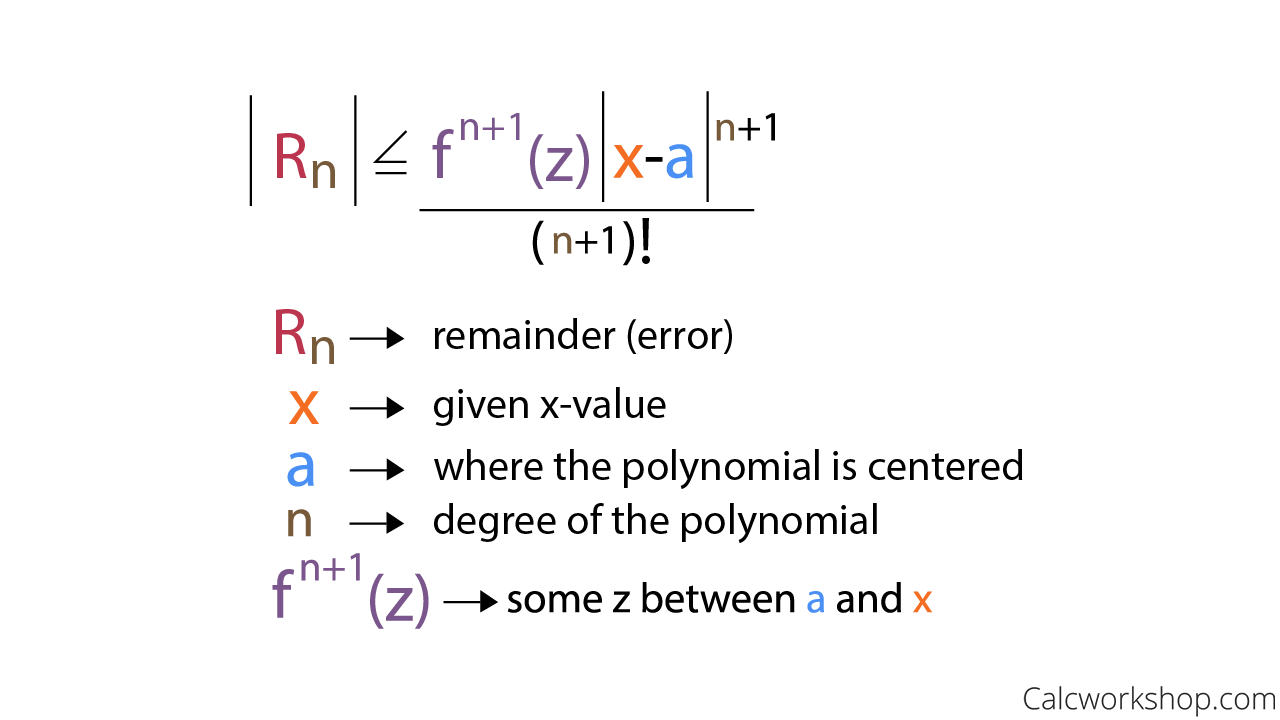Table of Contents
Over the past few weeks, some users have encountered the famous lagrange error message. This problem can occur for many reasons. Now let’s discuss some of them.
Approved
A specific Lagrange error (also called Taylor’s remainder theorem) can help us determine the academic form of the Taylor / Maclaurin polynomial to use to approximate a given error limit function.
The Guaranteed Lagrange Error (also known as the Taylor Remainder Theorem) can help us determine the degree of the Taylor/Maclaurin polynomial used to give an absolute approximation of a function given a particular error. See how this is done when evaluating a sine function. Lagrange error limit
In the previous tutorial series, Taylor showed us how to create a polynomial (Taylor-Taylor Series) using our center, which helps us create a radius and an interval of unity, derivatives, and factorials. We learned
also yours, there are five basic Taylor/Maclaurin expansion formulas. Have we learned how my family and I can quickly apply formulas to create new, more complex Taylor-Easy polynomials. We also
But any Taylor or McLaren series will always have an error form, simply because we don’t explicitly create a polynomial that already has an infinite number of terms.
Approved
The ASR Pro repair tool is the solution for a Windows PC that's running slowly, has registry issues, or is infected with malware. This powerful and easy-to-use tool can quickly diagnose and fix your PC, increasing performance, optimizing memory, and improving security in the process. Don't suffer from a sluggish computer any longer - try ASR Pro today!

Well, as far as this lesson is concerned, we will learn that most of them are three different: errors
Essentially, this lesson allows us to see how close the function’s human Taylor polynomials are to and hopefully we can make sure that all (small) errors are minimal.
It is also very important to understand what error is usually defined as the absolute value of the difference between a person’s true value and his approximation.
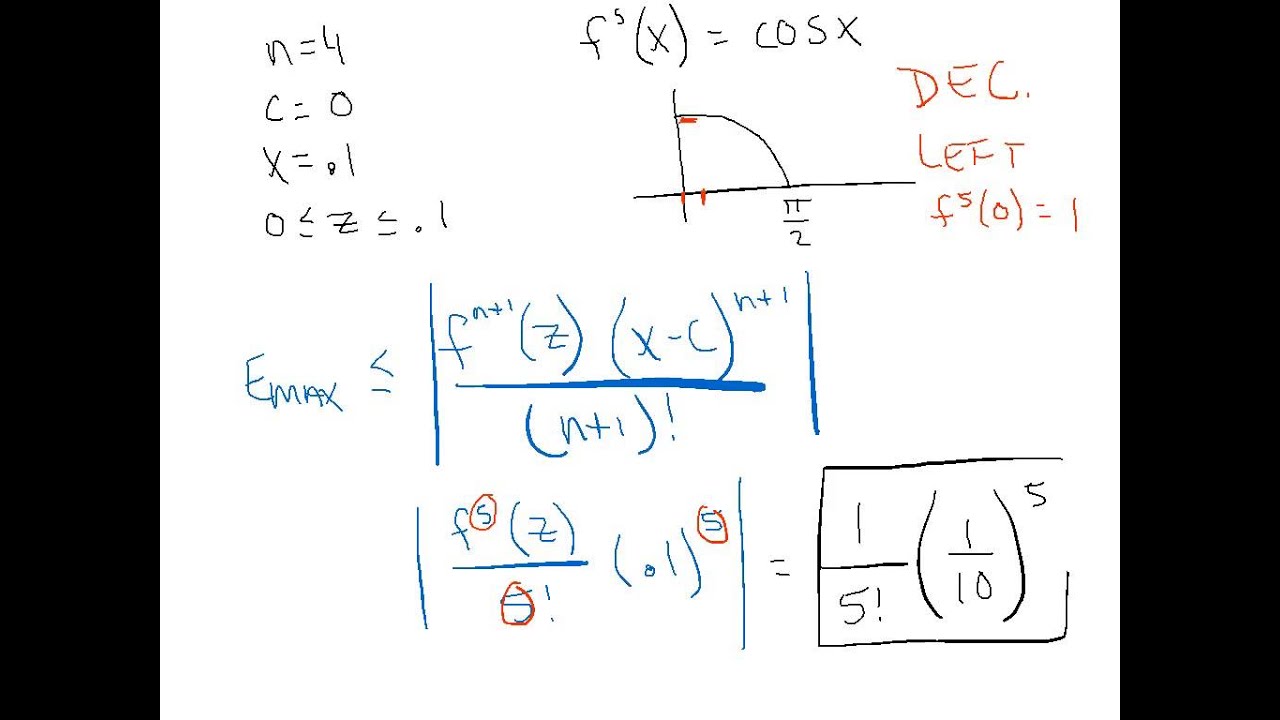
The upper limit for the fourth principal derivative of the period [0,1] is esin (1).
Sometimes it’s easy to figure out and calculate, and sometimes it’s a real problem.
So sometimes we tend to settle for the Lagrangian worst-case scenario: the associated error. Solving the error of the Lagrange boundary gives us A range of which method would be the big error, exactly without locating it.
At the current points, the formula cannot be used quickly. Fortunately, after rewriting my formula to make it more understandable, we can clearly see that it simply looks up your current maximum value in the main interval, so you can see this mit and other improved Lagrange error formulas. Related.< /p >
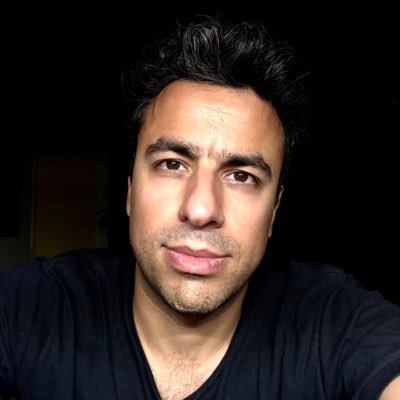
which follows from 1a: Let f usually be a function that is continuous and also has all derivatives in addition to this continuous function. Let Pn(x) be the Taylor approximation of order x from f(x) taken from A at the point , and let this error function be En(x)=f(x) − Pn(x). Then: Sa |en(x)|≤m(n+1)!|
At the end of this tutorial, you can be sure that Lagrange’s fallacy is extremely efficient, practical, and easy to find. Also, as Lynn McMullin explains, we will soon see that the variable series error or the Lagrange error will give us control over the error. Our big plus when constructing Taylor polynomials.
Lagrangian Error Limit – Video
The Lagrange error limit will be as follows: let f be its continuous function, which also has all its derivatives continuously. Let Pn (x) be the Taylor approximation of order n of the function f (x) centered at a, and let the strength of the error En (x) = f (x) – Pn (x). Then: | In (x) | ≤M (n + 1)! |
Subscribe to get more samples and over 350 HD videos
Monthly and even yearly plans
Get my subscription now
Examples of Lagrangian error bounds
Video Transcript
– [Instructor] Estimate the sine of 0.4 using Maclaurin polynomials,What is the lowest college education that provides a polynomialerror less than 0.001? So what are we really talking about here? Well, many people could take on a feature themselves and then improve it using the nth number.degrees of the Maclaurin polynomial, in fact, we could talk about the Taylor polynomial much more broadly,but let’s just say it’s a hundredth powerMaclaurin polynomial, but this is not requiredperfect approximation, there will be somea mistake or a little rest. And so we could call it the remainder of this Nth polynomial quality of malorin, and that would helpwhichever for any given x. Well we want ifthe criteria used for the exact problem could beso to speak. what We, it means, look whenLet’s take a sub sine of 0.4, okay if necessaryequal to our Maclaurin, the nth human degree of MaclaurinA polynomial marked as 0.4 plus the remainder of the remainder if the remainder of the N-power is Maclaurin.Polynomial score, with 0.4 and what we really wantdo to find out what the lowest degree isa particular polynomial So? How about letting me do it in person in a different color scheme. We want to understand whatwhat is the smallest n, what is actually the smallest n such that its remainder of the Nth power of ours is a Maclaurin polynomialthe 0.4 weighted value is less different from this number,less than 0.001? So it’s just another wayrephrase your problem. And how could weWe can do it, we have the ability to use what is called the Lagrangian fallacy trick, and we have other films that prove it, also called the rule.Taylor’s remainder theorem. And I’ll write it first and try to explain how I writeI’m leaving, but any time check the detailswhile working on it. So Taylor’s remainder theorem or Legrange’s error tells us that if m plus atethDerived from our function, very f, so this is her nplus the derivative of our function just in caseThe absolute value of this number is reduced by at least M for the open interval, the open interval on which our polynomial is based, in which case it is zero, weI’m going to use the Maclaurin case, so it actually contains zero and x, as well as zero and x, ha, which we are dealing with in clear this video, are 0.4, but I will speak in general for any x , so the following if true if ournplus the derivative of our function, just in caseits absolute value is a sum less than or equal toM, on the open interval containing our base location, would be C if we ever spoke there.in the general case, and the back button, which means to the right x